Phone:
(+65)8319-0742
Scaffolds are essential tools in construction, providing workers with access to elevated areas. However, their improper use can lead to serious accidents. Ensuring stability is critical to maintaining a safe work environment.
A scaffold consists of a platform and supporting structures designed to hold workers and materials. When these structures are moved incorrectly, they can become unstable, posing significant risks. Understanding the proper setup and usage is vital for preventing accidents.
This article will explore expert safety tips and guidelines under OSHA standards. By following these practices, construction sites can ensure the protection of their employees and reduce the likelihood of incidents.
Key Takeaways
- Scaffold stability is crucial for worker safety.
- Improper movement can lead to accidents and injuries.
- Platforms and supporting structures must be securely set up.
- OSHA guidelines provide essential safety standards.
- Regular inspections help maintain scaffold integrity.
Introduction to Scaffold Safety
Safety on construction sites starts with understanding the basics of scaffold usage. Scaffolds are critical for accessing elevated areas, but their improper handling can lead to severe accidents. Ensuring stability and compliance with safety standards is essential for protecting workers.
Construction companies and regulatory bodies prioritize scaffold safety to prevent injuries and fatalities. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) sets specific requirements for scaffold erection, movement, and usage. These guidelines are designed to minimize risks and create a secure work environment.
Before starting any scaffold work, it’s crucial to understand all requirements. Ignoring safety measures can result in unstable structures, leading to accidents. OSHA’s standards emphasize the need for proper training and regular inspections to maintain scaffold integrity.
A competent person plays a vital role in enforcing safety on the job site. This individual is responsible for identifying hazards, ensuring compliance, and addressing potential risks. Their expertise helps maintain a safe environment for every employee.
Key terms like “load capacity,” “guardrails,” and “fall protection” will be explored in later sections. Understanding these concepts is fundamental to implementing effective safety practices. By adhering to OSHA’s guidelines, construction teams can ensure the well-being of their workers and avoid costly incidents.
Understanding Scaffold Components and Terminology
Every scaffold is made up of specific components that ensure its stability and safety. Knowing these parts and their functions is crucial for maintaining a secure work environment. Misunderstanding or improper use of these components can lead to accidents and injuries.
Key Parts and Definitions
A scaffold consists of several essential parts. The bearer is a horizontal member that supports the platform. The putlog is a short horizontal piece that connects the scaffold to the structure. These components work together to distribute weight and maintain balance.
Another critical element is the body harness, which is part of fall protection systems. It ensures worker safety by preventing falls from elevated platforms. Understanding these terms helps workers communicate effectively and follow safety protocols.
Industry Glossary Insights
Construction workers must be familiar with industry-specific terminology. For example, a suspension scaffold is a platform hung from overhead structures. Knowing these terms ensures proper use and reduces the risk of misunderstandings on the job site.
Common mistakes include misidentifying parts or using them incorrectly. For instance, using a putlog in place of a bearer can compromise stability. OSHA standards provide clear guidelines for the correct use of each component, ensuring a safe work environment.
Proper use of scaffold parts is essential for maintaining safety. Regular inspections and adherence to OSHA standards help prevent accidents. By understanding these components and their roles, workers can contribute to a safer construction site.
Overview of OSHA Standards and Guidelines
OSHA standards play a critical role in ensuring scaffold safety on construction sites. These regulations, outlined in OSHA 1910.28, provide detailed guidelines for scaffold erection, use, and modifications. Compliance with these rules is essential for minimizing risks and protecting workers.
One key aspect of OSHA 1910.28 is the emphasis on scaffold stability. The standard specifies maximum load capacities and permissible spans for planks. For example, scaffolds must support at least four times their intended load. This ensures they can handle unexpected weight without compromising safety.
Guardrails are another critical requirement. OSHA mandates that guardrails be installed between 38 and 45 inches high for platforms over 10 feet. This measure significantly reduces the risk of falls, a common hazard on construction sites.
Adhering to these standards not only mitigates risks but also ensures worker protection. For instance, a competent person must inspect scaffolds before each shift. This proactive approach helps identify potential issues before they escalate.
Industry examples highlight the importance of compliance. Sites that follow OSHA guidelines experience fewer accidents and improved safety records. By understanding and implementing these standards, construction teams can create a safer work environment for everyone.
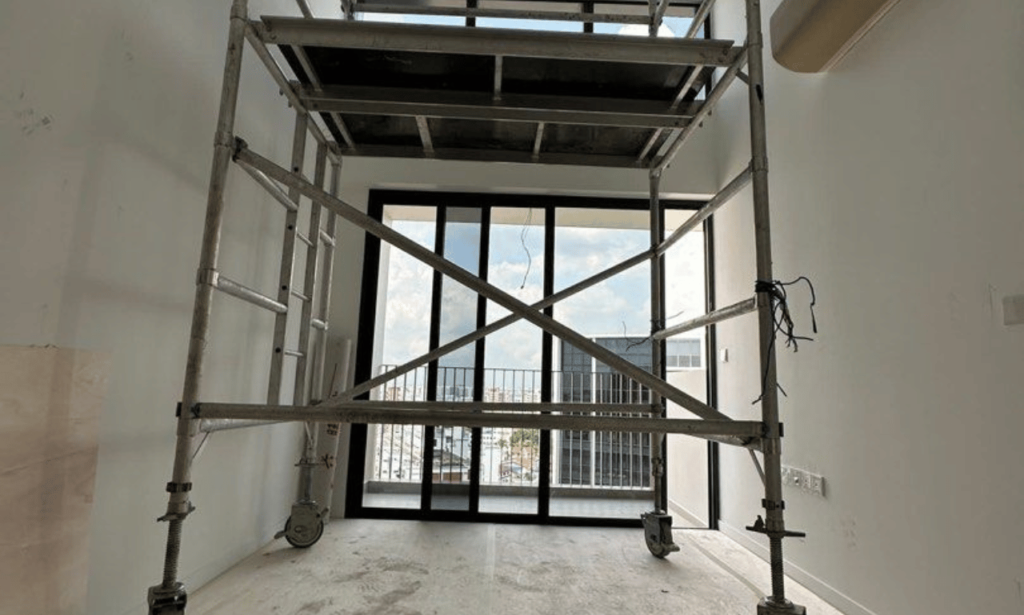
scaffolds shall not be moved horizontally – A Critical Safety Practice
Maintaining stability during scaffold operations is a cornerstone of construction safety. One of the most critical rules is that scaffolds must never be shifted horizontally while in use. This practice is strictly prohibited by OSHA regulations to prevent accidents and ensure worker protection.
Shifting a scaffold horizontally can compromise its structural integrity. Even a slight movement can destabilize the platform, endangering everyone on it. This is why OSHA emphasizes that all adjustments must be made when the scaffold is unoccupied and properly secured.
Workers might attempt horizontal movement to gain better access to a specific area. However, this approach is extremely hazardous. Instead, proper planning and supervision should ensure that the scaffold is positioned correctly before use. This minimizes the need for adjustments during operations.
OSHA standards highlight that each scaffold movement requires careful evaluation. A competent person must oversee any changes to ensure they align with safety protocols. This includes verifying that the scaffold remains stable and secure at all times.
Safety should always come first in scaffold-related activities. By adhering to these guidelines, construction teams can prevent accidents and create a secure work environment. For more detailed safety practices, refer to the Occupational Health and Safety Code.
Pre-Movement Assessment and Inspection Procedures
Pre-movement inspections are critical to maintaining scaffold stability and worker safety. Before any relocation, a thorough assessment ensures that the structure remains secure and compliant with OSHA standards. This procedure minimizes risks and prevents accidents during scaffold operations.
Checking Scaffold Stability
Stability is the foundation of scaffold safety. Begin by inspecting the base supports to ensure they are level and secure. Check for any signs of wear or damage that could compromise the structure. A competent person should verify that all components, including platforms and guardrails, are in proper condition.
OSHA guidelines require that scaffolds support at least four times their intended load. This ensures they can handle unexpected weight without failure. Regular inspections are essential to maintain this standard and prevent accidents.
Identifying Unstable Supports
Unstable supports are a major hazard in scaffold operations. Look for signs of shifting or uneven weight distribution. Use a checklist to ensure all connections are tight and secure. This procedure helps identify potential issues before they escalate.
For example, a construction site in New York experienced a scaffold collapse due to unstable supports. The incident highlighted the importance of rigorous inspections and adherence to safety protocols.
- Inspect base supports for stability and levelness.
- Verify the condition of platforms and guardrails.
- Check connections for tightness and security.
- Ensure compliance with OSHA load capacity standards.
Visual and technical assessments by a competent person are essential. This methodical approach minimizes risks and ensures a safe work environment. For more detailed guidelines, refer to the C/VM2 Verification Method.
Proper Set-Up and Grounding Techniques
Establishing a stable foundation is the first step in ensuring scaffold safety. Proper set-up begins with selecting the right equipment and following a specific order to avoid instability. A well-grounded structure reduces the risk of collapse and unexpected movement.
Grounding and anchorage are critical for maintaining stability. According to OSHA, scaffolds must be tied to the structure when the height exceeds four times the minimum base dimension. This ensures the structure can withstand external forces like wind or uneven weight distribution.
Using the correct equipment is essential. Base plates, mudsills, and leveling jacks help create a secure foundation. Regular inspections by a competent person ensure all components are in good condition and properly installed.
“A well-grounded scaffold is the backbone of construction safety. It prevents accidents and ensures worker confidence.”
Training plays a vital role in safe set-up practices. Workers must understand the importance of following the correct order during assembly. This includes securing base supports, installing guardrails, and verifying load capacities before use.
For more advanced techniques, refer to guidelines on flying scaffolding, which emphasize secure transportation and proper installation. By adhering to these best practices, construction teams can ensure a safe and efficient work environment.
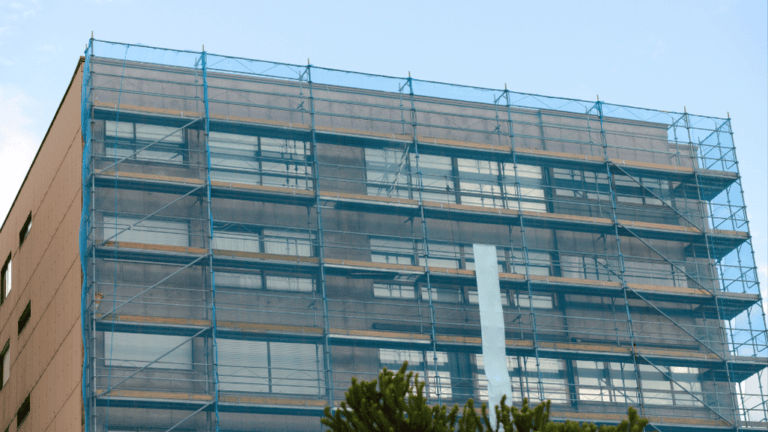
Safe Scaffold Erection and Dismantling Practices
Proper scaffold erection and dismantling are vital for ensuring workplace safety. These processes require careful planning, adherence to OSHA guidelines, and a focus on minimizing risks. By following step-by-step procedures, construction teams can ensure a secure environment for every employee.
Step-by-Step Safety Procedures
Erecting a scaffold safely begins with selecting the right equipment. Inspect all components for damage before assembly. Ensure the base is level and secure, using base plates or mudsills for stability. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions and OSHA measures to avoid errors.
During dismantling, start from the top and work downward. Remove platforms, guardrails, and supports systematically. Conduct safety checks at each stage to prevent accidents. A competent person must oversee the entire process to ensure compliance with national standards.
Common Errors and Prevention
One frequent mistake is skipping inspections before assembly or dismantling. This can lead to unstable structures and accidents. Another error is improper use of components, such as using a putlog instead of a bearer. Always follow the correct sequence and double-check connections.
“Safety is not just a protocol; it’s a mindset. Every step in scaffold handling must prioritize worker protection.”
OSHA and National Best Practices
OSHA mandates that scaffolds support at least four times their intended load. This measure ensures stability under unexpected weight. Guardrails must be installed on platforms over 10 feet high to prevent falls. These national guidelines are essential for maintaining safety.
For more detailed procedures, refer to the guide on safe scaffold erection and dismantling. This resource provides comprehensive steps to ensure compliance and worker safety.
By adhering to these practices, construction teams can minimize risks and create a safer work environment. Proper training and supervision are key to successful scaffold operations.
Guidelines for Secure Scaffold Usage in Construction
Adhering to secure scaffold usage guidelines is essential for construction site safety. These protocols ensure workers are protected from accidents and injuries. By following OSHA standards, construction teams can create a safer environment for everyone involved.
Improper scaffold usage can lead to severe injury or even fatalities. For example, failing to secure platforms or overloading structures can cause collapses. Such situations highlight the importance of strict adherence to safety guidelines.
To prevent accidents, workers must follow a checklist for secure scaffold usage. This includes verifying load capacities, ensuring proper guardrail installation, and conducting regular inspections. A competent person should oversee these checks to maintain compliance.
“Safety is not just a rule; it’s a responsibility. Every scaffold must be used correctly to protect lives.”
Case studies show that deviations from guidelines often result in workplace injuries. For instance, a construction site in Texas experienced a scaffold collapse due to improper assembly. This situation could have been avoided with proper training and adherence to OSHA standards.
Regularly reviewing usage guidelines with staff is crucial. It ensures everyone understands the importance of safety measures. This practice prevents dangerous situations and reduces the risk of costly mishaps.
For more detailed guidelines on scaffold safety, visit our scaffold access and egress page. By following these protocols, construction teams can ensure a secure and efficient work environment.
Employee Training and Competent Person Requirements
Effective training programs are the backbone of scaffold safety in construction. Proper education ensures that workers understand the risks and protocols associated with scaffold usage. Every company must prioritize training to prevent accidents and comply with OSHA standards.
OSHA mandates that employees receive training on scaffold hazards, including fall protection and electrical risks. This education helps workers use tools correctly and safely. A well-trained workforce is essential for maintaining a secure work environment.
Role of the Competent Person
A competent person plays a critical role in scaffold safety. This individual is responsible for identifying hazards, ensuring compliance, and overseeing scaffold operations. Their expertise ensures that structures remain stable and secure.
Training modules often include handling and preventing unsafe movements, such as shifting a scaffold shall moved horizontally. These programs reduce the risk of accidents and improve overall safety. Successful training initiatives have significantly lowered incident rates on construction sites.
“Training is not just a requirement; it’s a commitment to worker safety. Every company must invest in robust programs to protect their employees.”
- Stress the importance of employee training in preventing scaffold accidents.
- Define the role and qualifications of the competent person.
- Explain how proper training ensures safe tool usage.
- Describe the responsibilities of the competent person in evaluating scaffold conditions.
- Discuss training modules for preventing unsafe movements.
- Include examples of successful training programs.
- Emphasize the obligation of every company to implement training protocols.
By adhering to these guidelines, construction teams can ensure a safer work environment. Proper training and supervision are key to preventing accidents and maintaining compliance with OSHA standards.
Recognizing and Mitigating Hazardous Movements
Identifying and addressing hazardous movements is critical for maintaining a safe construction site. Recognizing these risks early can prevent serious accidents and ensure compliance with OSHA standards. By understanding the types of dangerous movements and how to mitigate them, workers can create a safer environment.
One key step is to test scaffold stability under simulated conditions. This involves applying weight to the structure to ensure it can handle its intended load. Regular stability checks help identify potential weaknesses before they become hazards.
During safety inspections, contractors should ask critical questions. For example, “Are all components securely fastened?” or “Is the base level and stable?” These inquiries help uncover issues that might otherwise go unnoticed.
To grade potential hazards, assess their likelihood and impact. High-risk issues, such as unstable supports, require immediate attention. Lower-risk concerns, like minor wear, can be addressed during routine maintenance.
“Proactive hazard recognition is the foundation of scaffold safety. It ensures risks are identified and mitigated before they escalate.”
Mitigating risks involves several steps. First, ensure all components are properly installed and inspected. Second, train workers to recognize and report unsafe conditions. Finally, implement continuous monitoring to address issues as they arise.
Scenarios like minor shifts in scaffold alignment can lead to dangerous outcomes. For instance, a slight tilt might seem harmless but could destabilize the entire structure. Addressing these issues promptly prevents accidents.
For more detailed guidance on scaffold safety, visit our scaffold access and safety page. By following these practices, construction teams can ensure a secure and efficient work environment.
Essential Equipment and Tools for Scaffold Safety
The right equipment is vital for maintaining safety during scaffold operations. Using the correct tools ensures stability and compliance with OSHA standards. Proper equipment not only prevents accidents but also enhances efficiency on the job site.
Essential tools include base plates, mudsills, and leveling jacks. These components provide a secure foundation, which is the purpose of ensuring stability. Without them, the structure could become unstable, posing significant risks.
Specialized tools like torque wrenches and plumb bobs are also crucial. They help in aligning and securing scaffold components during assembly. Their purpose is to ensure precise installation, reducing the likelihood of errors.
Inadequate tools can compromise scaffold integrity. For example, using worn-out components or improper fasteners can lead to collapses. This highlights the need for regular inspections and high-quality equipment.
“The right tools are not just accessories; they are necessities for ensuring worker safety and scaffold stability.”
In emergency situations, tools like fall arrest systems and guardrails are essential. These devices protect workers from falls, fulfilling the purpose of safeguarding lives. Proper training on their use is equally important.
Industry standards emphasize the need for equipment that meets OSHA specifications. For instance, guardrails must be installed on platforms over 10 feet high. This ensures compliance and reduces the risk of accidents.
In one case, a construction site avoided a potential collapse by using high-quality base plates and mudsills. This example underscores the importance of investing in proper equipment. Routine checks and maintenance further enhance safety.
For both routine and emergency scenarios, the need for reliable tools cannot be overstated. By adhering to OSHA guidelines and using the right equipment, construction teams can ensure a safer work environment.
Step-by-Step Guide for Safe Scaffold Handling
Ensuring safety during scaffold handling requires a systematic approach. Proper planning, execution, and verification are critical to maintaining a secure workplace. This guide outlines essential steps to prevent accidents and ensure compliance with safety standards.
Preparation and Planning
Before any scaffold movement, thorough preparation is necessary. Start by inspecting all components for damage or wear. Verify that the base is level and secure, using base plates or mudsills. This ensures stability and reduces the risk of a shift during operations.
Next, review the load capacity to ensure it meets OSHA standards. A scaffold must support at least four times its intended load. This precaution prevents overloading, which is a common reason for accidents.
- Inspect components for damage or wear.
- Verify base stability and levelness.
- Check load capacity and compliance with OSHA standards.
Post-Movement Verification
After moving the scaffold, conduct a detailed inspection to confirm its stability. Ensure all connections are tight and secure. Look for any signs of misalignment or imbalance that could compromise safety. This step is crucial to address potential shifts in load distribution.
Document the inspection results and share them with the team. This practice ensures accountability and maintains a safe workplace. Regular training on these procedures helps workers stay vigilant and proactive.
“A systematic approach to scaffold handling is the foundation of workplace safety. It ensures risks are minimized and compliance is maintained.”
By following these steps, construction teams can ensure a safe and efficient work environment. Proper handling and verification are key to preventing accidents and protecting workers.
Immediate Actions When Damage or Weakness is Detected
Detecting damage or weakness in scaffolding demands immediate action to ensure safety. Any delay can lead to catastrophic accidents, endangering workers and compromising the integrity of the structure. OSHA standards emphasize that scaffolding with defects must not be used until repairs are completed.
When a user identifies damage, the first step is to halt all operations. Notify a competent person immediately to assess the situation. This individual is trained to evaluate structural integrity and determine the next steps. OSHA requires that any scaffolding with defects be tagged and removed from service until it is repaired or replaced.
Securing the area is critical to protect employees. Barricade the affected zone and restrict access to prevent unauthorized use. Clear communication ensures everyone understands the risks and avoids the area until it is deemed safe.
“Prompt action is not just a protocol; it’s a commitment to worker safety. Every defect must be addressed immediately to prevent accidents.”
Real-life examples highlight the importance of swift action. In one case, a construction site avoided a potential collapse by identifying and repairing a cracked support beam. This quick response saved lives and reinforced the value of vigilance.
OSHA mandates specific inspection and repair criteria. Scaffolding must be inspected before each shift and after any incident that could affect its stability. Repairs must meet manufacturer specifications and OSHA standards to ensure safety.
Fostering a culture of safety is essential. Encourage users to report any issues without fear of reprisal. Immediate remediation of defects ensures a secure work environment and protects everyone on-site.
For more detailed guidelines on scaffolding safety, visit our bridge scaffolding page. By following these practices, construction teams can maintain a safe and efficient workplace.
Additional Tips for Working in Adverse Conditions
Adverse weather conditions can significantly impact scaffold safety, requiring extra precautions to maintain stability. High winds, icy platforms, and slippery surfaces pose unique challenges that demand specific strategies. OSHA guidelines emphasize the importance of adapting safety measures to these conditions to protect workers.
High winds can destabilize structures, so it’s crucial to secure all components tightly. Use additional ties or braces to reinforce the scaffold. Verify the function of safety equipment, such as guardrails and harnesses, to ensure they remain effective under stress.
Icy or slippery surfaces increase the risk of falls. Apply anti-slip coatings or use platforms with textured surfaces. Maintain a proper ratio of precautionary measures, such as adding extra guardrails or reducing the number of workers on the scaffold during severe weather.
Evidence-based practices suggest scheduling work during milder weather conditions whenever possible. If severe weather is unavoidable, take frequent breaks to reassess safety. Proactive maintenance, such as clearing ice or snow, is essential to prevent accidents.
“Safety in adverse conditions is not optional; it’s a necessity. Every precaution must be taken to ensure worker protection.”
For more detailed strategies on maintaining stability in challenging environments, explore our guide on proper stacking practices. By following these tips, construction teams can ensure a safer work environment, even in less-than-ideal conditions.
Case Studies and Examples from National Standards
Learning from past incidents is crucial for improving scaffold safety standards. Real-world examples and case studies provide valuable insights into the consequences of improper practices and the benefits of adhering to safety protocols. These lessons have shaped current guidelines and reinforced the importance of vigilance in construction environments.
Real-World Scenarios
One notable case involved a construction site where improper scaffold movement led to a collapse. Workers attempted to shift the structure horizontally while it was occupied, violating OSHA standards. This action resulted in injuries and highlighted the need for strict compliance with safety protocols.
In another instance, a site avoided disaster by following proper procedures. A competent person identified unstable supports during a routine inspection. Immediate corrective action ensured the scaffold remained secure, preventing potential accidents.
Lessons Learned
These incidents underscore the importance of training and supervision. Workers must understand the risks associated with improper scaffold use. Providing clear options for addressing issues, such as halting operations or seeking expert assistance, can prevent accidents.
Industry experience shows that proactive measures, like regular inspections and adherence to OSHA standards, significantly reduce risks. Feedback from competent persons has been instrumental in refining safety protocols and improving overall site safety.
“Every incident is an opportunity to learn and improve. By analyzing past mistakes, we can create safer environments for future projects.”
For more detailed insights, refer to OSHA documentation and industrial maintenance guides. These resources provide comprehensive strategies for maintaining scaffold safety and preventing accidents.
Conclusion
Ensuring safety in construction requires strict adherence to established protocols and guidelines. A competent person plays a vital role in maintaining the integrity of the scaffold platform, ensuring it remains stable and secure throughout its use. OSHA standards provide a clear framework for inspections, training, and proper setup, which are essential for preventing accidents.
Key takeaways include the importance of regular inspections, proper training for all employees, and the need to avoid unsafe practices. The competent person oversees these processes, ensuring compliance and addressing potential hazards promptly. By following these measures, construction teams can create a safer work environment.
Commitment to safety is not just a requirement but a responsibility. Continuous inspection, training, and adherence to OSHA guidelines are crucial for protecting lives and maintaining workplace safety. A well-informed approach ensures that every operation on the scaffold platform is conducted with care and precision.