Phone:
(+65)8319-0742
The journey towards excellence is an ever-evolving quest that beckons continuous improvement through what experts call Progressive Skill Acquisition. At the heart of this technique lies the commitment to dive deeper into the art of Skill development – a task both exhilarating and complex. Ambitious learners and seasoned professionals alike can benefit from this systematic approach that redefines the boundaries of their capabilities and reshapes the landscape of Learning process mastery. It’s time to embrace this structured pathway to personal growth and unleash a world of potential.
Key Takeaways
- Progressive Skill Acquisition is a stepping stone for expanding your talent and expertise.
- An individualized, nuanced approach is critical for effective Skill development.
- Learning process mastery is not a destination, but a journey of constant evolution.
- Adapting learning strategies to personal and situational needs enhances skill acquisition.
- Real growth comes from challenging existing boundaries through progressive techniques.
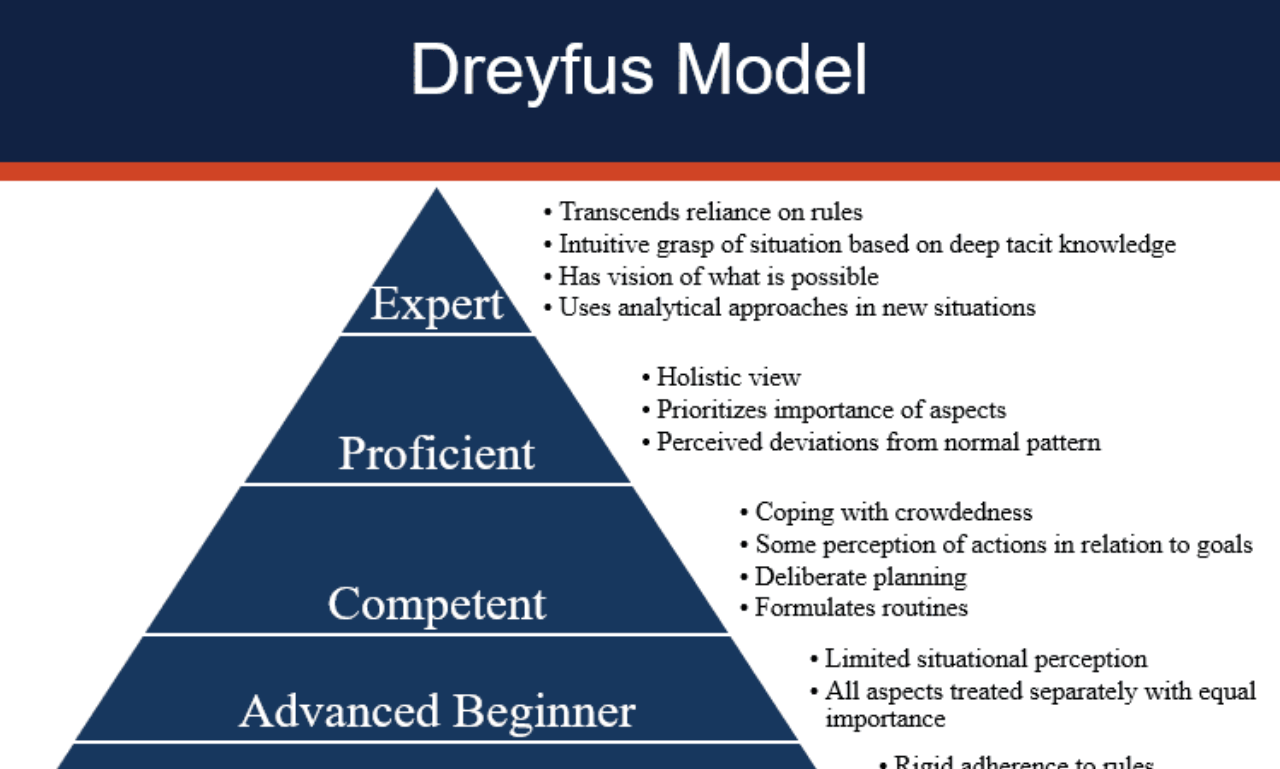
Understanding the Foundations of Progressive Skill Acquisition
As we delve into the intricate world of Progressive Skill Acquisition, it is crucial to recognize the underlying theories and applications that guide our understanding and practices. This journey intersects the domains of both Advanced skill enhancement and cognitive theory, shaping the way we process information and react within various environments.
The Dynamic Relationship Between Theory and Practice
At its heart, Progressive Skill Acquisition lies in the harmonious relationship between Information Processing (IP) and Ecological Dynamics (ED). These theoretical frameworks offer unique lenses through which practitioners understand how skills are learned, honed, and retained. IP emphasizes the role of the mindâs cognitive structures, whilst ED encourages an integrated view of movement within a physical context.
Exploring Information Processing (IP) and Ecological Dynamics (ED)
When dissecting these pivotal concepts, Information Processing champions the idea of the human mind resembling a computer, processing inputs and yielding outputs. On the other side, Ecological Dynamics posits that humans are dynamic systems interacting constantly with their ever-changing environments. Both theories are essential to crafting sophisticated methods for skill enhancement.
Pragmatism in Skill Development: Context Matters
The art of pragmatic skill development rests on the adaptability of learning strategies to suit the learner’s environment and needs. By adopting a context-based learning approach, instructors can tailor experiences that reflect the real-world scenarios in which skills will be applied, thus fostering a deeper level of understanding and adaptability.
| Aspect | Information Processing (IP) | Ecological Dynamics (ED) |
|---|---|---|
| Fundamental Theory | Cognitive interpretation of sensory input to direct action | Continuous interaction between organism and environment |
| Focus in Learning | Sequential stages of information analysis | Adaptation to environmental constraints |
| Role of Context | Important in shaping cognitive processes | Crucial as a determinant of movement behavior |
| Practical Application | Drills focused on decision-making and pattern recognition | Variable practice that mimics real-life situations |
In conclusion, the exploration of advanced skill enhancement is multifaceted, requiring a synthesis of theory and practice. Providing a wealth of strategies, from comprehensive process models to biofeedback, the advancements in skill acquisition open new vistas for learners and educators alike. By embracing the complexity of Information Processing and Ecological Dynamics, and through the lens of pragmatic development, one can navigate the intricate tapestry of learning with sophistication and efficacy.
Assessing Your Skill Level for Personalized Learning

Embarking on a journey of skill enhancement calls for a meticulous understanding of where one currently stands. It’s not just about pursuing skill growth methods with vigor; it’s about doing so with insight and strategy. Before we delve into the heart of personalized learning, letâs consider the significance of nuanced skill assessment.
Identifying Individual Constraints and Abilities
Every learner presents with a unique set of abilities and faces distinct individual constraints that can either hinder or bolster their learning process. In the realm of progressive skill acquisition, recognizing these factors is the first step toward crafting a learning experience that resonates with the individual. These factors encompass physical, cognitive, and emotional traits that when understood, enable a bespoke approach to skill development.
Your assessments must not only register capacity but also constraints which might include limited time, access to resources, or even psychological barriers. Identifying these helps to apply personalized learning techniques that circumnavigate limitations while exploiting strengths.
Adapting to Variability Based on Skill Stage
As one progresses through the spectrum of skill acquisition, from novice to expert, the learning approach must also evolve. Skill stage adaptation calls for an educational design that accommodates the shifting demands of the learner’s evolving skill set. In the initial stages, a structured environment where basic techniques are established might be essential, giving way to more complex, variable conditions that test and refine these skills as one advances.
Here’s where the assessment of skill stage comes into playâit’s not static but an ongoing process. As learners demonstrate growth, educators and mentors are tasked with introducing new challenges that reflect real-world conditions, thereby solidifying the learner’s competency and dynamic problem-solving abilities.
Designing Effective Learning Environments for Skill Mastery

Creating an optimal learning environment design is fundamental for fostering a student’s enhanced learning progression. Environments engineered with the learner in mind put forth a framework that prioritizes not only the acquisition but also the skill mastery optimization. Tailoring these spaces to suit individual needs can lead to more profound, lasting learning with real-world applications. It involves a holistic view of the learning process, appreciating its complexity and crafting conditions that propel students towards success.
A well-designed learning environment coalesces around three critical aspects to engage and challenge learners effectively: the individual’s attributes, environmental factors, and the nature of the tasks at hand. By manipulating these variables, educators can cultivate a space that is conducive to concentrated practice and cognitive growth. This multifaceted approach ensures that learners are not just memorizing procedures but achieving authentic skill mastery that is adaptable and resilient.
- Individual Attributes: Recognizing the unique learning styles, strengths, and areas for improvement in each student.
- Environmental Factors: The physical and social setting must be safe, supportive, and free from distractions to promote uninterrupted learning.
- Task Nature: Implementing activities that are both engaging and align with the intended learning outcomes.
Moreover, the collaboration between educators and learners helps in creating an engaging platform where feedback is immediate, and adaptability is ingrained in the process. Through the strategic design of learning experiences, students can navigate through diverse challenges, enhancing their capacity to transfer skills learnt to new and unexpected contexts. With the ultimate goal being an autonomous learner, equipped not just with knowledge, but with a robust, transferable skill set.
Progressive Skill Acquisition: Evolving Mastery Strategies

In the realm of skill acquisition, a paradigm shift is taking place. Traditional methods which heavily relied on rote repetition are being surpassed by more effective strategies. These strategies understand that step-by-step skill improvement is not just about repeating an action but about embedding it within realistic scenarios for enriched learning experiences. This encapsulates the heart of what we refer to as representative learning design, a method that drastically enhances skill uptake by mirroring the complexities of real-world application.
Shifting from Repetitive to Representative Learning
The transition from purely repetitive practice to representative learning design acknowledges the robust nature of the environments in which skills are actually used. By integrating representative tasks within the learning process, we are able to promote the continuum of repetition necessary for proficiency while simultaneously ensuring learners can apply their skills under varying conditions. This symbiosis between practice and application is where true mastery begins to blossom.
Navigating the Continuum of Repetition and Variability
Navigating the delicate balance between repetition and variability is much like walking a tightrope. Too much repetition may lead to skills that are rigid and inflexible, while excessive variability can prevent the deep engrainment of essential actions. The secret lies in the intelligent design of practice routines that align with the learnerâs current developmental stage.
| Developmental Stage | Repetitive Practice Emphasis | Representative Variability Emphasis |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Learning | Moderate | Low |
| Intermediate Development | Low | Moderate |
| Advanced Refinement | Low | High |
As displayed in the table, it’s crucial for the learning process to evolve. Where early stages may demand more structure and repetition to build a foundation, advanced stages thrive on high levels of variability that challenge and refine the learner’s skills. Throughout this journey, step-by-step skill improvement paves the way towards achieving not just competence, but also creative and adaptable expertise.
Neuroscience Insights into Skill Development and Retention
Neuroscience has become an indispensable ally in our quest for neuroscientific skill enhancement, revealing the entwined relationship between neurocognition and skill retention. Brain’s plasticity, or its ability to change throughout an individual’s life, has monumental implications for learners and educators aiming to master new abilities. Each time we engage in learning a new skill, our brain’s neural networks adjust and strengthen, paving the way for improved performance and skill endurance.
Automaticity, a concept at the core of neurocognition, refers to the point at which a skill becomes second nature. The transition from deliberate, conscious control to fluid, unconscious performance is a hallmark of deep learning. As we contemplate progressive skill acquisition, the goal is to reach a level of automaticity where skills can be executed with minimal cognitive load. This leaves more mental resources available for complex problem-solving and adaptation to new challengesâa clear edge in any endeavor.
Implicit learning, another valuable concept borrowed from neuroscience, offers a pathway to enduring skill retention by embedding knowledge deep within the subconscious. This approach nurtures an environment where learning occurs naturally, without the need for explicit awareness. Furthermore, embracing practice that’s spaced and variedâcontrastive to rote, blocked repetitionâenables cognitive engagement that forges robust motor pathways. By leveraging such neuroscientific approaches to practice, individuals can achieve a more profound, lasting mastery that is transferable to the diverse and unpredictable nature of real-world situations.
FAQ
What is Progressive Skill Acquisition?
Progressive Skill Acquisition is a methodical approach focusing on a **continuous learning process** and **step-by-step skill improvement** to enhance personal capabilities. It’s about advancing skills through a deliberate strategy that adapts to changing needs and contexts, emphasizing **learning process mastery** and **evolving mastery strategies**.
How do theory and practice intersect in skill development?
Theory and practice are intertwined in skill development, with theoretical frameworks like **Information Processing (IP)** and **Ecological Dynamics (ED)** influential in shaping practice methods. Understanding these relationships can lead to more **advanced skill enhancement** and effective **context-based learning**.
Why is understanding the context important in pragmatic skill development?
Context is crucial in pragmatic skill development because it influences the applicability and success of various skills. Tailoring skill development strategies to the environment and the learner’s current abilities leads to more relevant and practical outcomes, enhancing the overall **learning environment design**.
What are some key personal constraints that should be considered for personalized learning?
Key personal constraints include physical, mental, and emotional traits or conditions that could impact learning. Identifying and understanding these allows for more **personalized learning techniques** and **skill stage adaptation**, which are fundamental aspects of **Progressive Skill Acquisition**.
How does variability affect skill acquisition?
Variability plays a vital role in Progressive Skill Acquisition by preparing learners to adapt to different situations. Adapting training to reflect the variability of real-life scenarios helps with the transfer and retention of skills, enhancing both cognitive and motor skills for better performance.
Can you explain the shift from repetitive to representative learning?
The shift from repetitive to representative learning is a key **evolving mastery strategy** in Progressive Skill Acquisition. Repetitive learning focuses on rote repetition, while representative learning integrates practice with scenarios that closely mimic real-life conditions, fostering skill transferability and adaptability.
Why is it important to find a balance between repetition and variability in practice?
Finding a balance between repetition and variability is essential for effective skill development. While repetition helps build confidence and muscle memory, variability ensures that the skills are resilient and adaptable. This balance is critical for learners to achieve **skill mastery optimization**.
How does neuroscience contribute to our understanding of skill development?
Neuroscience contributes to our understanding of skill development by revealing how the brain acquires and retains new skills. The brain’s plasticity enables the refinement of movements and cognitive functions, allowing for **neuroscientific skill enhancement** and optimizing **skill retention** through principles such as automaticity and implicit learning.