Phone:
(+65)8319-0742
Scaffolding is a crucial component in various industries, providing workers with access to heights for different tasks. However, it can also pose significant risks if not used properly. In this guide, we’ll explore the do’s and don’ts of telescopic scaffolding, ensuring safety and efficiency in your projects. We’ll cover important aspects such as ensuring a level and stable surface, using correct components and materials, inspecting before use, accessing the scaffold using the 3T method, and following manufacturer’s instructions. Additionally, we’ll discuss the importance of proper training, compliance with scaffolding standards, and checking the scaffolding tag before use.
Key Takeaways:
- Telescopic scaffolding is vital for accessing heights safely in various industries.
- Proper use of telescopic scaffolding involves ensuring a level and stable surface.
- Inspecting the scaffold before use and following manufacturer’s instructions is essential.
- Using the 3T method and providing proper training are crucial for safety.
- Compliance with scaffolding standards and checking the scaffolding tag enhances safety.
The Dos of Telescopic Scaffolding
When working with telescopic scaffolding, it is crucial to follow certain guidelines to ensure a safe and secure work environment. By adhering to these dos, you can minimize the risk of accidents and maximize the efficiency of your scaffolding system.
1. Ensure a Level and Stable Surface
To guarantee the stability of the scaffolding, it is essential to set it up on a level and stable surface. This will prevent any shifting or instability during use. Take the time to prepare the ground and make necessary adjustments before erecting the scaffold.
2. Use Correct Components and Materials
Make sure to use the correct components and materials designed specifically for telescopic scaffolding systems. Using the wrong components can compromise the integrity of the scaffold and pose a safety risk. Always follow the manufacturer’s recommendations and guidelines.
3. Inspect Before Use
Before each use, conduct a thorough inspection of the scaffolding to identify any potential issues or damages. Check for loose or missing parts, cracks, and signs of wear. If any problems are detected, do not use the scaffold until the necessary repairs have been made.
4. Follow the 3T Method
When accessing the scaffold, always use the 3T method (Through the Trapdoor): maintain three points of contact at all times, either two feet and one hand or two hands and one foot. This method ensures stability and reduces the risk of falls.
5. Respect Load Capacity
Do not exceed the recommended load capacity of the telescopic scaffolding. Overloading the scaffold can lead to structural failure and potential accidents. Make sure to distribute the load evenly and stay within the prescribed limits.
6. Work on Protected Platforms
Ensure that the scaffolding platform is equipped with guardrails and toe boards to provide a protected working area. These safety features prevent falls and protect workers from potential hazards.
7. Follow Manufacturer's Instructions
Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions for the proper assembly and use of the telescopic scaffolding. Deviating from the recommended procedures can compromise the structural integrity of the scaffold and jeopardize safety.
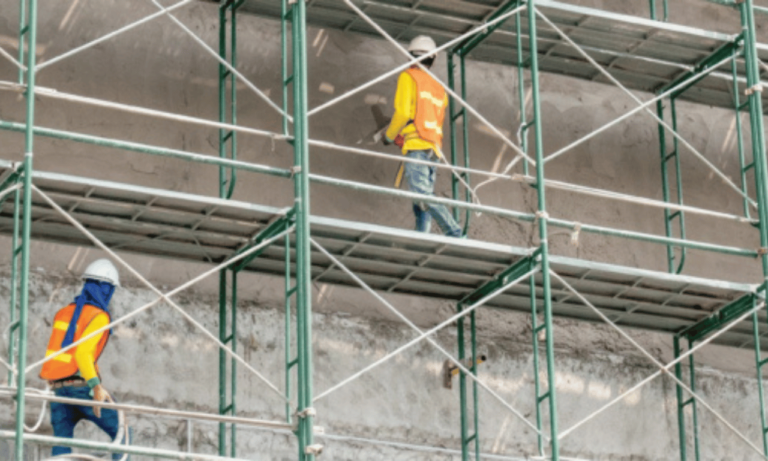
8. Provide Proper Training
Ensure that all workers using the telescopic scaffolding receive adequate training on its proper use, safety procedures, and potential hazards. Proper training reduces the likelihood of accidents and ensures that everyone understands how to work safely with the equipment.
9. Comply with Scaffolding Standards
Stay informed about the latest scaffolding standards and regulations applicable in your industry. Staying compliant with these standards ensures that your telescopic scaffolding meets the required safety criteria.
10. Check the Scaffolding Tag
Before each use, check the scaffolding tag for inspection status and load capacity. This tag provides essential information about the scaffold’s safety and compliance. Do not use the scaffold if the tag indicates it is not safe for use.
By following these dos of telescopic scaffolding, you can create a safer work environment and ensure the efficient and secure use of your scaffolding system.
The Don'ts of Telescopic Scaffolding
While using telescopic scaffolding, it’s crucial to be aware of certain practices to avoid that can compromise safety. By steering clear of these don’ts, you can ensure a secure working environment and prevent accidents.
1. Overloading the Tower
One of the most critical don’ts is to **avoid overloading** the scaffolding tower beyond its designated load capacity. Exceeding the weight limits can lead to structural instability and potential collapses, endangering the workers on the platform.
2. Using Red Tag Scaffolding
**Red tag scaffolding**, which indicates it’s been deemed unsafe, should never be used. If you come across scaffolding with a red tag, it is crucial to report it to the relevant authorities or supervisors and refrain from using it until it has been inspected and certified as safe for use.
3. Moving the Tower with Occupants
Under no circumstances should you attempt to move the scaffolding tower with occupants still on the platform. This practice can cause imbalance, instability, and potential falls, putting the safety of the workers at risk. Always ensure that the tower is completely stationary and secure before allowing anyone to access or exit the platform.
4. Using an Unstable Scaffold on Unstable Ground
It’s important to avoid using a telescopic scaffold on ground that is **uneven or unstable**. Placing a scaffold on such surfaces can lead to instability, tilting, or collapse. Always ensure that the base of the scaffold is on a stable and level surface to maintain structural integrity and prevent accidents.
5. Making Makeshift Components or Unauthorized Modifications
**Making makeshift components or unauthorized modifications** to the telescopic scaffold should be strictly avoided. Alterations that are not approved by the scaffold manufacturer can compromise its structural integrity and lead to instability or collapse. Always use components and accessories specifically designed for the scaffolding system.
6. Leaving an Unattended Scaffold
Leaving a scaffold unattended for an extended period of time is another practice to avoid. **An unattended scaffold** can be subject to unauthorized use, vandalism, or accidental damage. Workers should ensure that the scaffold is secured, locked, or removed when not in use to prevent accidents or unauthorized access.
7. Working in Adverse Weather Conditions
Lastly, it’s crucial to avoid working on scaffolding in **adverse weather conditions** such as high winds, heavy rain, snow, or icy conditions. Inclement weather can compromise the stability of the scaffold and increase the risk of accidents. Always monitor weather conditions and halt work on the scaffold if conditions become unsafe.
Benefits of Telescopic Scaffolding

Telescopic scaffolding offers a wide range of benefits in construction and maintenance projects.
1. Access to Heights
Telescopic scaffolding provides safe and reliable access to heights, enabling workers to reach areas that would be difficult or unsafe to access otherwise. This allows for efficient completion of tasks at elevated levels, leading to increased productivity and project success.
2. Adjustable Heights
With its adjustable height feature, telescopic scaffolding offers flexibility and convenience. It allows workers to easily adapt the scaffolding to different height requirements, eliminating the need for multiple scaffolding setups. This saves time and effort, enabling workers to focus on the task at hand.
3. Safe Work Environment
Telescopic scaffolding creates a safe work environment by incorporating safety barriers such as guardrails and toe boards. These features help prevent falls and provide protection from falling objects, ensuring the well-being of workers at elevated heights. Prioritizing the safety of workers is crucial in any construction or maintenance project.
4. Better View
Working at heights can sometimes hinder visibility, making it challenging to carry out tasks effectively. Telescopic scaffolding offers a better view, allowing workers to have a clear line of sight and increased visibility of their working area. This enhanced visibility facilitates precise and efficient work execution.
5. Strong Structure
Telescopic scaffolding is built with a strong and sturdy structure, providing stability and reliability. This ensures the safety of workers and peace of mind during work at elevated heights. A robust scaffolding structure is essential in maintaining a secure and stable working platform, enabling workers to focus on their tasks without concerns about stability issues.
| Benefits of Telescopic Scaffolding |
|---|
| Access to heights |
| Adjustable heights |
| Safe work environment |
| Better view |
| Strong structure |
Types of Telescopic Scaffolding and Their Components

Telescopic scaffolding is available in different types to suit various construction and maintenance needs. The two main types of telescopic scaffolding are supported scaffolds and suspended scaffolds. Supported scaffolds are secured in place by fixed materials like poles or frames, while suspended scaffolds are suspended from cables or ropes, providing access to heights in a more versatile manner.
Telescopic scaffolding can be constructed using different materials, each with its own advantages and characteristics. The most common materials used for telescopic scaffolding include aluminum, fiberglass, steel, and wood. Aluminum scaffolding is lightweight, durable, and corrosion-resistant, making it an ideal choice for various applications. Fiberglass scaffolding offers high electrical resistance and is suitable for projects in areas with electrical hazards. Steel scaffolding provides exceptional strength and stability, making it suitable for heavy-duty construction projects. Wood scaffolding is commonly used for smaller construction projects and offers a cost-effective solution.
Components are essential parts of telescopic scaffolding, working together to ensure a stable and secure working platform. These components include standards, toe-boards, ledgers, bracing, base plates, transoms, couplers, boarding, and guardrails.
The standards are the vertical members that form the main structural framework of the scaffolding. Toe-boards are installed around the edges of each platform level to prevent tools or materials from falling. Ledgers are horizontal tubes that connect the standards, providing additional stability. Bracing is used to reinforce the scaffolding structure, ensuring it remains rigid and secure. Base plates are placed at the bottom of each standard to provide stability and even weight distribution. Transoms are horizontal members that provide support for the scaffold boards. Couplers are used to connect various components together securely. Boarding refers to the platforms where workers stand while working at heights. Guardrails are essential for worker safety, preventing falls from elevated platforms.
When these components are properly assembled and combined with the appropriate type of telescopic scaffolding, they provide a safe and reliable working platform for construction and maintenance tasks.
| Type | Material | Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| Supported Scaffold | Aluminum | Lightweight, durable, corrosion-resistant |
| Fiberglass | High electrical resistance | |
| Steel | Exceptional strength, stability | |
| Wood | Cost-effective | |
| Suspended Scaffold | Aluminum | Lightweight, versatile |
| Fiberglass | High electrical resistance | |
| Steel | Heavy-duty, durable | |
| Wood | Flexible, cost-effective |
Conclusion
Telescopic scaffolding is an essential tool in various industries, providing workers with safe and efficient access to heights during projects. By following the proper use guidelines, prioritizing safety, providing adequate training, and ensuring compliance with scaffolding standards, a secure work environment can be created for successful project completion.
It is crucial to prioritize safety by following the manufacturer’s instructions, conducting regular inspections, and providing proper training to all workers. Adhering to safety guidelines and compliance with scaffolding standards ensures the efficient use of telescopic scaffolding.
With proper training and compliance with safety protocols, workers can confidently utilize telescopic scaffolding to achieve their project goals while maintaining a safe work environment. Remember, safety should always be the top priority, and when applied correctly, telescopic scaffolding can enhance productivity and efficiency while ensuring the well-being of all workers involved.
FAQ
What are the dos of telescopic scaffolding?
The dos of telescopic scaffolding include ensuring a level and stable surface, using the correct components and materials, conducting a thorough inspection before use, accessing the scaffold using the 3T method (Through the Trapdoor), putting the load within the prescribed limits, working on protected platforms with guardrails and toe boards, following the manufacturer’s instructions for assembly and use, providing proper training for workers, complying with scaffolding standards, and checking the scaffolding tag for inspection status and load capacity.
What are the don’ts of telescopic scaffolding?
The don’ts of telescopic scaffolding include not overloading the scaffold beyond its load capacity, avoiding the use of scaffolding with a red tag indicating it’s unsafe, not moving the tower with occupants on the platform, not using an unstable scaffold on uneven or unstable ground, avoiding the use of makeshift components or unauthorized modifications, not leaving a scaffold unattended for a long period of time, and avoiding the use of scaffolding in adverse weather conditions.
What are the benefits of telescopic scaffolding?
Telescopic scaffolding offers several benefits in construction and maintenance projects. It provides safe access to heights, allowing workers to reach areas that would be difficult or unsafe to access otherwise. The adjustable height feature ensures flexibility and convenience. Telescopic scaffolding creates a safe work environment with safety barriers such as guardrails and toe boards, preventing falls and providing protection from falling objects. Its strong structure offers stability and reliability, ensuring the safety of workers while working at heights.
What are the different types of telescopic scaffolding and their components?
Telescopic scaffolding comes in different types, including supported scaffolds and suspended scaffolds. Supported scaffolds are held in place by fixed pieces of material such as poles or frames, while suspended scaffolds are suspended from cables or ropes. The types of telescopic scaffolding materials include aluminum, fiberglass, steel, and wood. Each type has its unique advantages and characteristics. The components of telescopic scaffolding include standards, toe-boards, ledgers, bracing, base plates, transoms, couplers, boarding, and guardrails. These components work together to provide a stable and safe working platform.

















