Phone:
(+65)8319-0742
Scaffolding safety is key in the construction world. Workers use these temporary setups to reach high places. It’s vital to follow scaffolding dimensions and safety rules to keep everyone safe. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has clear guidelines for scaffolding size and safety.
OSHA’s rules aim to keep workers safe from dangers on temporary structures. These rules cover things like platform decking, guardrails, and how much weight scaffolds can hold. Following these guidelines helps construction companies set up safe work areas and reduce the chance of accidents.
States also have their own laws to make scaffolding safer. These laws might be stricter because they address local issues. It’s important for everyone in construction to know both federal and state safety rules. This way, they can work in a safe environment.
Key Takeaways:
OSHA has established comprehensive guidelines for scaffolding dimensions and safety standards in the construction industry.
Scaffold platforms must be fully decked or planked and equipped with proper guardrails, midrails, and toe boards.
Scaffolds must be capable of supporting up to four times their maximum intended load.
State governments may introduce additional localized laws to strengthen scaffold safety protocols.
Employers and workers should familiarize themselves with both federal and state-level safety standards to ensure full compliance and maintain a safe working environment.
OSHA Scaffolding Safety Standards
Scaffolding safety is very important in construction. Every year, about 4,500 people get hurt and over 60 die from scaffolding accidents. To lower these numbers, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has set clear scaffolding safety guidelines. These rules are key for keeping workers safe when they’re working high up.
Fall Protection Requirements
OSHA’s scaffold safety regulations say workers over 10 feet up need to be safe from falls. They must use guardrails or a fall arrest system. Workers on certain scaffolds must use both guardrails and a fall arrest system.
A fall arrest system includes an anchor point, a body harness, and sometimes a lanyard or lifeline. This setup is vital for keeping workers safe on scaffolds.
Guardrail Height Specifications
OSHA’s scaffolding standards require guardrails on new scaffolds to be between 38 and 45 inches tall. Midrails must be halfway between the top rail and the platform. Following these guardrail height rules is key for protecting workers from falls.
Cross Bracing Guidelines
For cross bracing as a top rail, OSHA says it should be between 38 and 48 inches above the platform. If it’s a midrail, it should be 20 to 30 inches above. These cross bracing guidelines help ensure scaffolding systems are safe and stable.
Employers must make sure their scaffolding meets OSHA’s safety standards. This includes proper fall protection, guardrail height, and cross bracing. By focusing on worker safety and following these rules, the construction industry can greatly reduce accidents and deaths from scaffolding.
Scaffolding Dimensions and Load Capacities
Keeping scaffolding safe and stable is key. OSHA sets rules for how much weight scaffolds can hold. Light duty scaffolds can handle 25 pounds per square foot. Medium duty scaffolds can handle 50 pounds, and heavy duty scaffolds can handle 75 pounds.
Platform Planking Requirements
Planking is crucial for scaffolding safety. It must support at least four times its intended load plus its own weight. OSHA says planks can deflect no more than 1/60th of their length under load.
There are different types of planks for scaffolding. You can find scaffold grade lumber, steel, and aluminum planks rated for 50 lbs/sq ft and 75 lbs/sq ft. These meet the strict requirements for safety.
The span of scaffold planks depends on their load capacity and thickness. For 25 pounds/square foot, the span is 10 ft with full thickness lumber and 8 ft with nominal thickness. At 50 pounds/square foot, the span is 8 ft with full thickness and 6 ft with nominal thickness. Heavy duty scaffolds at 75 pounds/square foot have a span of 6 ft with full thickness lumber.
Scaffold Weight Capacities
Scaffolding size and weight capacity are vital for safety. Scaffolds and their parts must be strong enough to handle four times the maximum intended load without breaking. This ensures the platform can handle unexpected loads or stresses.
To prevent excessive deflection under heavy loads, you can double scaffold planking across spans with added weight. This spreads the load more evenly and lowers the risk of plank failure. Remember, don’t add outrigger platform weight to the main platform. This can overload the scaffold and harm its structure.
Scaffold Footing and Stability
The safety of scaffolding is key in construction. A good scaffold footing is vital. It must support loads and stand up to weather. The base’s size and shape are important for stability.
Rules say scaffolds should not be taller than four times their base length. This keeps them stable, even when it’s hard. Scaffold calculations and designs must think about the load, the work, and the scaffolding sizes needed.
Cal/OSHA says scaffolds over 36 feet need a permit. Scaffolds over 125 feet must be designed by a professional engineer. These rules show how important good scaffold design and expert help are.
Checking the scaffold often is key to keeping it stable. A skilled person should check it every day. They look at the load, structure, and dangers. In places with a lot of shifts, a person should be there for each one.
Weather like rain, snow, and wind can affect the scaffold. It’s important to think about this during checks.
“Understanding the complex engineering behind scaffolds can reduce the risk of incidents. Thorough oversight and attention to detail can significantly enhance scaffold safety.” – Scaffolding Safety Expert
Following rules, doing regular checks, and making sure the footing and base are right helps. Good building site equipment and safety rules prevent accidents. This keeps workers safe on scaffolds.
Scaffold Inspection and Maintenance
Regular checks on scaffolds are key to keeping workers safe and following the law. The Work at Height Regulations 2005 say scaffolds must be checked before use, after being set up, and every seven days. The HSE has a checklist for these inspections, which includes looking at the scaffold’s parts, making sure it’s level, and checking for guardrails.
These inspections must be done by someone who knows what they’re doing. They need to be trained, like with CISRS scaffold inspection courses. OSHA also says scaffolds must be checked by someone who knows what they’re doing before each shift and after any changes that could affect the scaffold’s safety.
Regular Inspection by Competent Person
A trained person must check the scaffold before each shift and after any changes. These checks help find problems early and keep everyone safe. They make sure the scaffold is set up right, the base plates are in place, and the scaffold can hold its load.
Reports from these inspections should include who did the check, when and where it was done, and what was found. There are three colors used for scaffolds: green for safe, yellow for caution, and red for danger.
Proper Cleaning and Maintenance Procedures
After each job, scaffolds need to be cleaned and checked for damage. Use a low-pressure washer with mild soap to avoid harming the structure. Keeping scaffolds in good shape helps them last longer and keeps everyone safe.
“Scaffold inspection and maintenance are critical aspects of ensuring worker safety and regulatory compliance in construction projects.”
Workers should tell the person in charge if they see any problems with the scaffolding. If there’s any doubt, the scaffold needs to be checked again. By following the right steps for scaffold inspection procedures and keeping scaffolds clean and well-maintained, construction sites can be safer for everyone.
Training Requirements for Scaffold Workers
Proper training is key for worker safety on scaffolds. With 2.3 million construction workers on scaffolds, it’s vital for employers and employees to know their roles in scaffold training.
OSHA requires employers to give thorough scaffold worker training to all staff on scaffolding. This training must include handling, hazard identification, control methods, load capacities, and safety rules. Employers must also provide the right personal protective equipment (PPE) like hard hats and safety harnesses.
Employer Responsibilities for Training
Employers are crucial in keeping workers safe with proper scaffold training. They must give detailed scaffold assembly instructions and scaffold erection guidelines. Regular refresher courses are also needed to keep skills sharp. If the worksite changes or if employees show they don’t understand, retraining is essential.
Worker Responsibilities for Safety
Workers must also focus on their safety and that of their colleagues. They should follow the worker safety responsibilities from their training. This includes wearing PPE, using fall arrest systems, and following scaffold assembly and dismantling rules. By doing so, workers can greatly reduce the risk of accidents and injuries.
“Scaffolding safety is a shared responsibility between employers and employees. Through comprehensive training, adherence to guidelines, and a commitment to best practices, we can create a safer work environment for all.” – John Smith, Safety Manager
In conclusion, scaffold training is essential for worker safety in construction. By meeting their employer training responsibilities and worker safety responsibilities, both can help create a safer work environment. This is crucial since scaffolding accidents cause about 4,500 injuries and 60 deaths each year in the U.S.
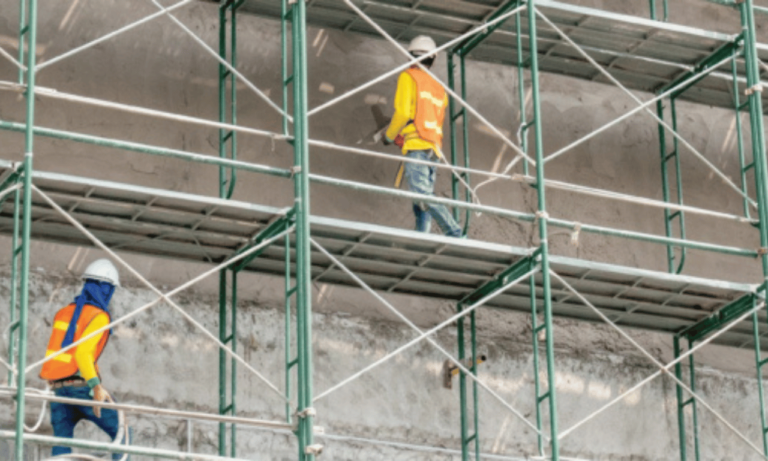
Personal Protective Equipment for Scaffolding Work
Working on scaffolding requires personal protective equipment (PPE) to keep workers safe. PPE for scaffolding includes items to protect against falls and falling objects. It’s designed for working at heights.
A fall arrest system is key for scaffolding safety. It includes a harness, connecting devices, and an anchor point. Fall protection starts at 10 feet, higher than the usual 6 feet in construction. Employers must provide the right fall arrest systems and ensure they’re used right.
Hard hats are also crucial for scaffolding work. They’re made to be light, adjustable, and comfortable. Hard hats protect against falling objects and should always be worn on scaffolds.
Workers should also use tool tethers to keep tools from falling. These lanyards attach to the worker’s belt or harness. They prevent tools from dropping if they’re accidentally released.
“Scaffolding is one of the top ten most frequently cited violations by OSHA, making proper use of personal protective equipment critical for worker safety.” – OSHA
Other important PPE for scaffolding includes eye, face, hand, and ear protection. These items not only protect but also improve comfort and dexterity. The variety of PPE shows a focus on meeting specific site needs in the scaffolding industry.
Pedestrian and Object Protection Measures
Keeping pedestrians and objects safe from falling debris is key in construction. A mix of protection layers is needed to reduce risks. Good pedestrian and falling object protection keeps everyone safe and the project running smoothly.
Scaffold barricades and danger zone signs are vital for pedestrian safety. They mark off the construction area and warn people of dangers. These barriers must be clear, strong, and far enough from scaffolding for safety.
Overhead Canopies and Debris Netting
Overhead canopies and debris netting also play a big role in safety. They catch falling objects, preventing harm or damage. OSHA rules require these to keep everyone safe from falling items.
Did you know that a falling 1-pound object from 6 feet can seriously hurt someone? This shows why debris netting and canopies are crucial. Safety nets must handle more weight than expected and cover the scaffold’s edge well.
Using a layered safety approach is key for safety. Scaffold barricades, danger signs, canopies, and netting work together. This way, construction sites can lower risks and keep everyone safe.
Conclusion
Scaffolding safety is key to keeping workers safe on construction sites. It helps prevent accidents. Following OSHA scaffolding rules is very important. These rules cover many things like fall protection and how stable the scaffolding is.
It’s also important to train workers well on scaffolding. Both employers and workers must work together to keep the site safe. This way, everyone knows their role in safety.
Construction companies often use scaffolding experts to meet these safety needs. These experts know the latest rules and how to keep scaffolding safe. This lets companies focus on their main work while the safety is handled by pros.
Keeping scaffolding safe is a team effort in the construction world. Following OSHA rules, training workers, and working with scaffolding experts are all important. This helps make the work site safer for everyone.
Investing in safety not only protects workers but also helps the project succeed. It makes the company look good too.