Phone:
(+65)8319-0742
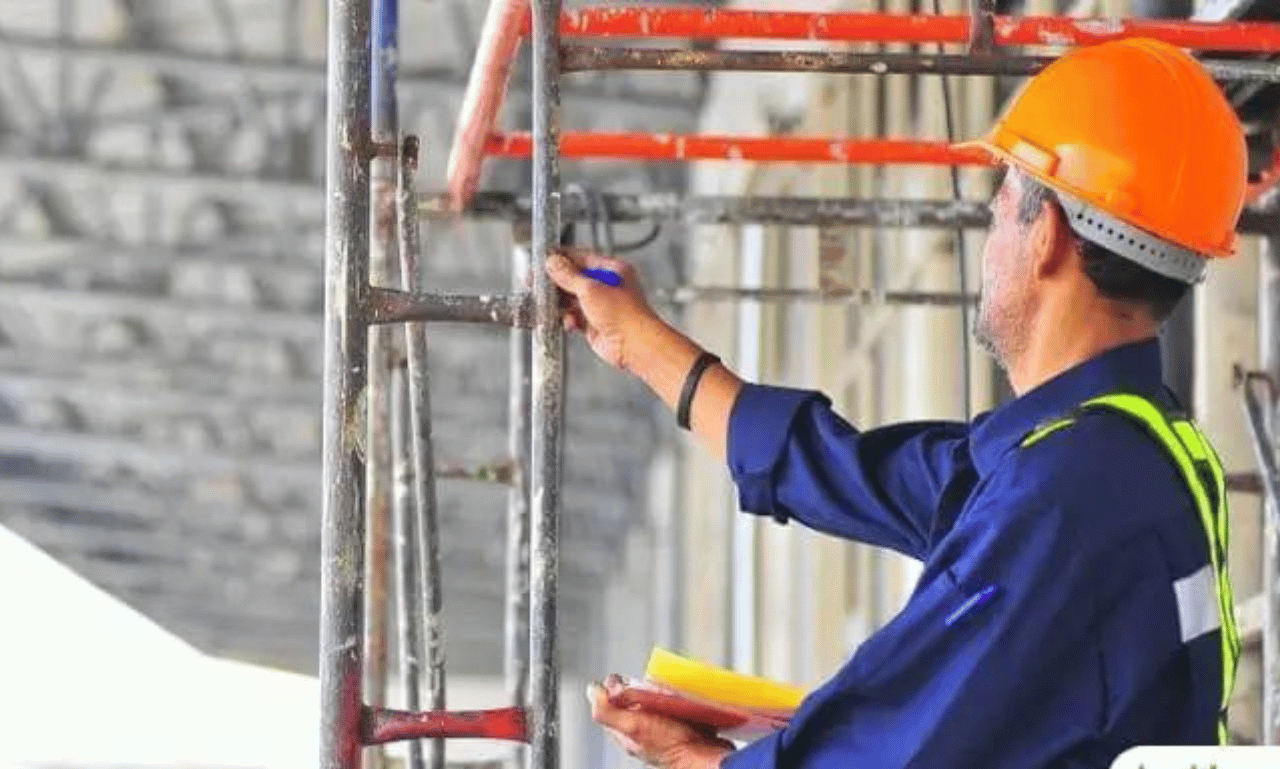
Welcome to our essential guide on daily scaffold pre-use checks. When it comes to scaffold safety in the workplace, following OSHA scaffold regulations and implementing best practices for scaffold inspections are crucial. By prioritizing regular checks and maintenance, you can ensure the safety and integrity of your scaffolds, minimizing the risk of accidents and creating a secure work environment.
In this guide, we will explore the importance of daily scaffold pre-use checks, provide an overview of OSHA scaffold regulations, and offer practical tips and best practices for conducting effective scaffold inspections. Whether you are a supervisor or a worker, this guide will equip you with the knowledge to ensure compliance and safety in the use of scaffolds.
Key Takeaways:
- Daily scaffold pre-use checks are essential for maintaining a safe work environment.
- Complying with OSHA scaffold regulations is crucial for scaffold safety.
- Regular inspections and proper maintenance can prevent accidents and ensure scaffold integrity.
- Following a scaffold inspection protocol and documenting inspections is important.
- Training and competence are key for effective scaffold inspections.
Understanding Scaffold Safety Measures
When it comes to scaffold safety, there are several essential measures that need to be understood and implemented. These measures are crucial for ensuring the well-being of workers and the integrity of the scaffold itself. In this section, we will explore the different safety measures that should be considered during daily scaffold pre-use checks, along with some valuable maintenance tips to keep the scaffold in optimal condition.
1. Secure and Stable Base
One of the fundamental safety measures is to ensure that the scaffold has a secure and stable base. This involves checking for proper leveling, supporting surfaces, and adequate foundations. A sturdy base provides a solid foundation and reduces the risk of the scaffold tipping or collapsing.
2. Guardrails and Toeboards
Installing guardrails and toeboards is another critical safety measure. These protective barriers help prevent falls and protect workers from potential hazards. Guardrails should be at least 42 inches in height and securely fastened to the scaffold structure. Toeboards, on the other hand, should be at least 4 inches in height and prevent objects from falling off the scaffold.
3. Safe Access and Egress
Providing safe access and egress to the scaffold is vital for both productivity and safety. Workers should have easy and secure means to enter and exit the scaffold, such as stairways or properly maintained ladders. Adequate access and egress prevent slips, trips, and falls during scaffold use.
4. Regular Inspection and Maintenance
Scaffold maintenance is key to ensuring its safety and longevity. Regular inspection and maintenance, both before and after each use, are essential. This includes checking for any signs of wear and tear, loose or damaged components, and addressing any issues promptly. Implementing routine maintenance practices can help identify potential hazards and prevent accidents.
5. Proper Load Capacity
Understanding the load capacity of the scaffold is crucial for maintaining safety. It is essential to adhere to the manufacturer’s guidelines and ensure that the scaffold is not overloaded. Overloading the scaffold can lead to structural failure and increase the risk of collapse. Workers should be educated about the maximum load capacity and strictly adhere to it.
By implementing these scaffold safety measures and following proper maintenance tips, workers can significantly reduce the risk of accidents and ensure a safe working environment. Now, let’s take a look at some maintenance tips in the next section.
Overview of OSHA Scaffold Regulations
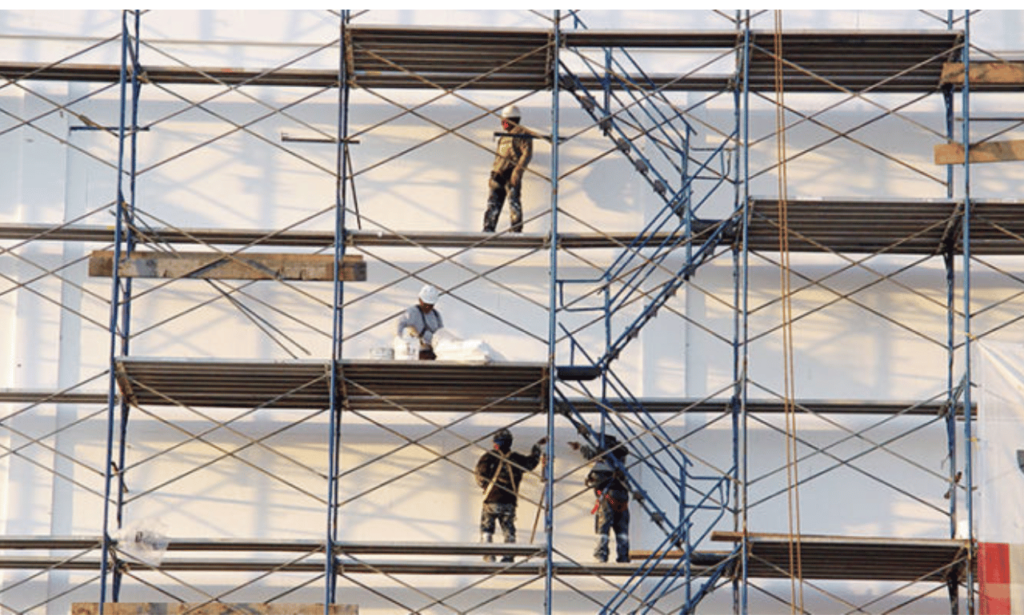

In order to maintain a safe and secure work environment, it is crucial for organizations to comply with OSHA scaffold regulations. These regulations serve as guidelines that ensure the proper construction, use, and maintenance of scaffolds, minimizing the risk of accidents and injuries on construction sites.
OSHA scaffold regulations cover a wide range of requirements, including:
- Platform construction and specifications: OSHA mandates that scaffold platforms must be able to support their own weight as well as four times the maximum intended load. Additionally, platforms should be at least 18 inches wide and have no more than 1-inch gaps between planks.
- Guardrails and toeboards: To prevent falls from scaffolds, OSHA requires the installation of guardrails that are at least 38 inches high. Toeboards are also important to prevent objects from falling off scaffolds and injuring workers below.
- Access and egress: Scaffold systems must have safe means of access and egress, such as stair towers or ladders. These access points should be secured and visibly marked to ensure easy navigation for workers.
- Stability and structural integrity: Scaffolds must be erected on solid foundations and should be able to withstand all anticipated loads without tipping or collapsing. All scaffold components, including frames, braces, and pins, should be free from defects and properly secured.
- Training and supervision: OSHA regulations also emphasize the importance of training and supervision in scaffold safety. Employers must ensure that workers receive adequate training, understand scaffold hazards, and are competent to perform their duties safely.
By complying with OSHA scaffold regulations, organizations can create a culture of safety and reduce the risk of accidents and injuries. It is crucial for employers, supervisors, and workers to stay updated on these regulations and implement them consistently.
| OSHA Scaffold Regulations | Key Requirements |
|---|---|
| Platform Construction and Specifications | Scaffold platforms must be able to support their own weight as well as four times the maximum intended load. Platforms should be at least 18 inches wide and have no more than 1-inch gaps between planks. |
| Guardrails and Toeboards | Guardrails that are at least 38 inches high must be installed to prevent falls from scaffolds. Toeboards should also be in place to prevent objects from falling off the scaffold. |
| Access and Egress | Scaffold systems must have safe means of access and egress, such as stair towers or ladders. |
| Stability and Structural Integrity | Scaffolds must be erected on solid foundations and able to withstand anticipated loads without tipping or collapsing. All scaffold components should be free from defects and properly secured. |
| Training and Supervision | Employers must ensure that workers receive adequate training and are competent to perform their duties safely. |
Adhering to OSHA scaffold regulations is not just a legal requirement, but also a crucial aspect of ensuring the well-being of workers. By understanding and implementing these regulations, organizations can create a safer work environment and mitigate potential hazards associated with scaffolds.
Steps for Conducting Scaffold Inspections
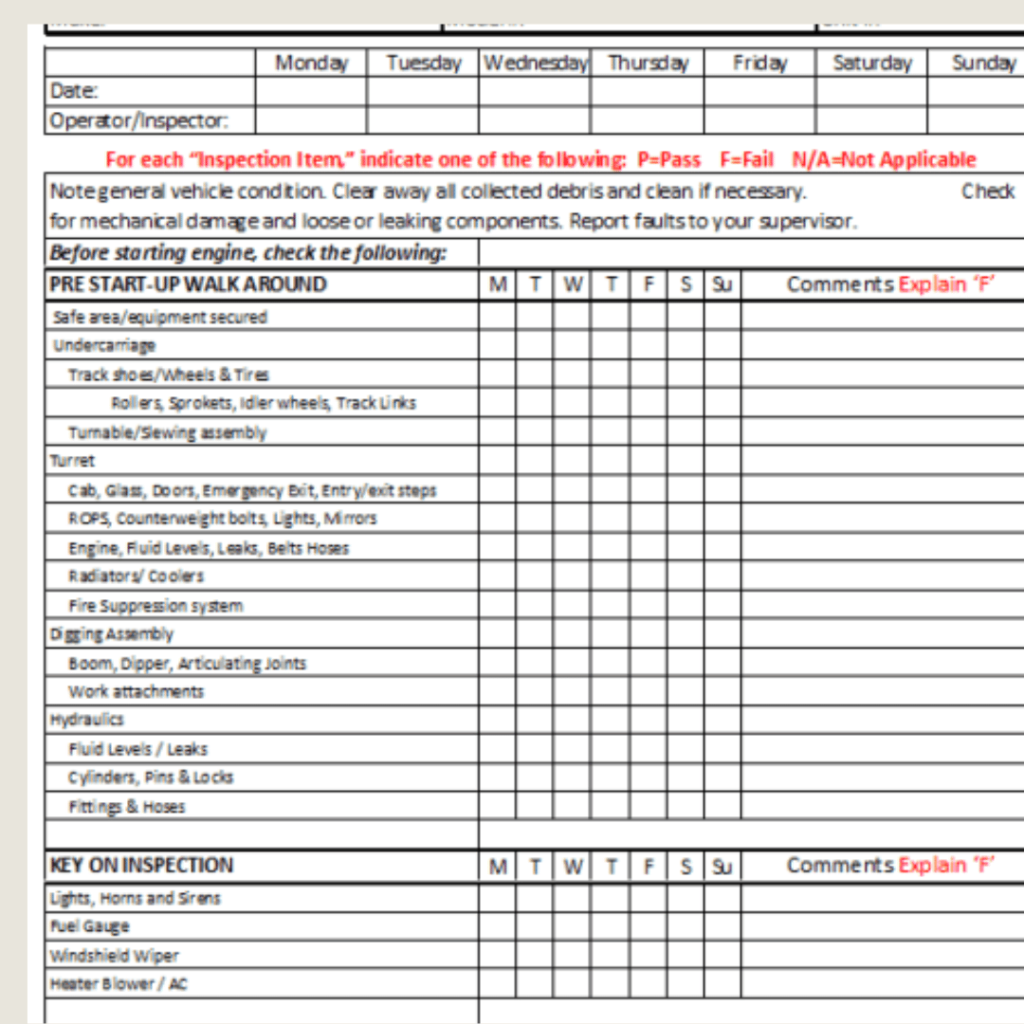
Conducting scaffold inspections is a crucial part of ensuring the safety and integrity of the structure. Follow these step-by-step guidelines to perform thorough scaffold inspections:
- Review the safety protocols: Before starting the inspection process, familiarize yourself with the established safety protocols and guidelines for scaffold inspections. This will help you understand what to look for and ensure compliance with regulations.
- Inspect the foundation: Begin by examining the scaffold’s foundation. Check for any signs of damage, such as cracks or unevenness, as this can compromise the stability of the scaffold.
- Check the structure: Evaluate the overall structure of the scaffold, including the frames, braces, and trusses. Look for any signs of wear and tear, corrosion, or loose connections that may pose a hazard.
- Assess the scaffolding platform: Inspect the platform for stability and secureness. Check for any missing or damaged planks, guardrails, or toeboards. Ensure that the platform is level and properly secured to prevent accidents.
Continue the inspection by assessing the following key areas and components:
- Scaffold accessories: Inspect all accessories, such as ladders, stairways, and access gates. Ensure they are in good condition and properly secured to the scaffold.
- Anchorage points: Verify the strength and stability of any anchor points used to secure the scaffold. Check for any signs of deterioration or damage that may compromise their effectiveness.
- Guardrails and fall protection: Examine the guardrails and fall protection systems to ensure they are properly installed, intact, and meet the necessary safety requirements.
- Inspect for electrical hazards: Identify any potential electrical hazards near the scaffold, such as overhead power lines. Ensure proper precautions are taken to prevent electrical accidents.
Remember to document your findings during the inspection process. This documentation will serve as a reference for future inspections and provide a record of compliance.
By following these scaffold inspection guidelines, you can identify potential hazards, address maintenance issues, and ultimately maintain a safe working environment for all individuals involved.
Pre-Use Scaffold Checklist

Before using a scaffold, it is crucial to perform thorough checks to ensure its safety and minimize the risk of accidents. This pre-use scaffold checklist serves as a comprehensive guide to help workers inspect and verify the integrity of the scaffold before commencing work.
1. Visual Inspection
Visual inspection is the first step in the pre-use scaffold checklist. Carefully examine the scaffold for any visible damage, such as cracks, bent or missing components, loose connections, or signs of wear and tear. Pay close attention to the platform, guardrails, and access points.
2. Stability Check
Check the stability of the scaffold by ensuring that it is securely anchored or tied off to prevent tipping or displacement. Verify that the scaffold is level and properly supported on a firm and stable surface. If the scaffold is erected on uneven ground, use appropriate leveling devices to ensure stability.
3. Load Capacity
Confirm the scaffold’s load capacity by referring to the manufacturer’s guidelines and OSHA regulations. Ensure that the scaffold can safely support the anticipated weight, including workers, tools, and materials. Avoid overloading the scaffold, as it can compromise its integrity and lead to accidents.
4. Guardrails and Fall Protection
Check that the scaffold is equipped with appropriate guardrails, midrails, and toeboards to prevent falls. Inspect the condition of these safety components, ensuring they are installed correctly and securely. Confirm the availability and functionality of fall protection equipment, such as harnesses and lifelines, if required.
5. Access Points
Inspect the scaffold’s access points, such as ladders, stairs, or ramps, to ensure they are properly secured and stable. Verify that the access points are clear, free from obstructions, and in good working condition. If using ladders, ensure they extend above the platform and have proper handholds.
6. Weather Conditions
Consider the prevailing weather conditions before using the scaffold. Adverse weather, such as high winds, rain, or snow, can affect the stability and safety of the scaffold. Avoid working on the scaffold during inclement weather or take appropriate measures to secure it against potential hazards.
7. Documentation and Training
Maintain proper documentation of scaffold inspections, including dates, findings, and any necessary corrective actions. Ensure that workers using the scaffold have received adequate training on scaffold safety, including the completion of regular checks and compliance with OSHA regulations.
By following this pre-use scaffold checklist, workers can proactively identify and address potential hazards, ensuring a safe and secure work environment. Regular inspections and adherence to safety protocols are essential to prevent accidents and maintain the integrity of scaffolds.
Best Practices for Scaffold Inspections
When it comes to ensuring the safety and integrity of scaffolds, following best practices for scaffold inspections is crucial. These practices not only help identify potential hazards but also contribute to a secure work environment for all workers involved. Here are some key best practices to consider:
1. Conduct Regular Inspections
Regular inspections are essential to catch any issues or defects in scaffolds before they can pose a risk. Frequency of inspections should align with the nature of work being carried out, but a general rule of thumb is to inspect scaffolds:
- Before initial use
- At least once every seven days
- After any events that may have affected the scaffold’s integrity, such as severe weather conditions or accidents
By conducting inspections at appropriate intervals, you can detect any potential problems early and take necessary corrective measures.
2. Document Inspection Findings
Documenting inspection findings is an integral part of best practices for scaffold inspections. Maintain thorough records that capture the dates, details, and outcomes of each inspection. This documentation not only helps track any recurring issues or patterns but also serves as evidence of compliance in case of any regulatory audits or inquiries.
3. Ensure Competence and Training
It is crucial to ensure that scaffold inspectors are competent and adequately trained. Training should cover areas such as identifying hazards, understanding OSHA regulations, and recognizing potential signs of scaffold deterioration or damage. By equipping inspectors with the necessary knowledge and expertise, you enhance the effectiveness and accuracy of inspections.
4. Include a Comprehensive Checklist
Developing a comprehensive inspection checklist is a best practice that ensures consistent and thorough examinations of scaffolds. The checklist should cover various critical elements, including:
- Structural components
- Guardrails and toeboards
- Access points and ladders
- Platform conditions
- Scaffold ties and bracing
- Weather protection
- Stability and plumbness
By following a checklist that encompasses all necessary inspection areas, inspectors can conduct systematic examinations and identify potential hazards or deficiencies more effectively.
By implementing these best practices for scaffold inspections, you can enhance the safety and reliability of scaffolds in your workplace. Remember, prioritizing regular inspections, documentation, competence, and comprehensive checklists can go a long way in preventing accidents and maintaining a secure work environment.
Ensuring Compliance with Scaffold Inspection Protocol
Complying with a scaffold inspection protocol is vital in maintaining a safe and secure work environment. Following a standardized protocol ensures consistent checks, record-keeping, and adherence to regulatory requirements. It is the responsibility of both supervisors and workers to prioritize scaffold safety through rigorous compliance with the inspection protocol.
The Role of Supervisors
Supervisors play an essential role in enforcing the scaffold inspection protocol. They should ensure that all workers are aware of the protocol’s guidelines and receive proper training on conducting thorough inspections. Supervisors must also regularly monitor scaffold inspections to verify compliance and address any deficiencies promptly. By prioritizing scaffold safety and maintaining a culture of vigilance, supervisors set the tone for compliance among the workforce.
The Responsibility of Workers
Every worker utilizing scaffolds should be familiar with the scaffold inspection protocol and actively participate in its implementation. They should consistently perform pre-use checks before each work session, identifying any potential hazards or signs of scaffold damage. Workers must promptly report any issues to their supervisors and refrain from using the scaffold until it is deemed safe for use. By actively engaging in scaffold inspections, workers contribute to a safer work environment for themselves and their colleagues.
To facilitate compliance with the scaffold inspection protocol, organizations should establish clear communication channels between supervisors and workers. Regular training sessions and safety meetings can reinforce the importance of inspections and provide an opportunity to address any concerns or questions. Encouraging open dialogue and fostering a safety-conscious atmosphere are key to maintaining compliance with the inspection protocol.
By adhering to a scaffold inspection protocol, supervisors and workers demonstrate a commitment to upholding scaffold safety standards. This proactive approach helps prevent accidents, minimize risks, and ensure the overall integrity of scaffolds within the workplace.
Conclusion
In conclusion, this article has provided an essential guide to daily scaffold pre-use checks, emphasizing the importance of following OSHA regulations and implementing best practices for scaffold inspections to maintain a safe and secure work environment.
By conducting thorough inspections and adhering to proper maintenance and safety measures, workers can prevent accidents and ensure the integrity of scaffolds. It is crucial to regularly inspect key areas and components of the scaffold, such as the platform, guardrails, and base, to identify any potential hazards or damage that may compromise worker safety.
Furthermore, a pre-use scaffold checklist can serve as a useful tool to ensure that all necessary checks are performed before using the scaffold. This checklist should include items such as verifying secure footing, examining the stability of the scaffold, inspecting the access points, and checking for proper signage and warning devices.
Lastly, it is essential to follow a scaffold inspection protocol and maintain proper documentation to ensure compliance and consistency in inspections. Regular training and competence of scaffold inspectors should be prioritized to ensure thorough inspections and accurate record-keeping.
FAQ
Why are daily scaffold pre-use checks important?
Daily scaffold pre-use checks are important to ensure the safety of workers who will be using the scaffold. These checks help identify any potential hazards or damage to the scaffold before it is used, minimizing the risk of accidents and injuries.
What are some scaffold safety measures that should be considered?
Some scaffold safety measures that should be considered include ensuring a solid foundation, secure access and egress points, proper guardrails, regular inspection and maintenance, and adequate training for workers who will be using the scaffold.
What are the key scaffold regulations set by OSHA?
OSHA has set several regulations pertaining to scaffolds, including requirements for scaffold design, construction, and use, as well as guidelines for fall protection, access, and egress. It is important to comply with these regulations to ensure a safe and compliant work environment.
How should scaffold inspections be conducted?
Scaffold inspections should be conducted systematically and thoroughly. This includes inspecting the scaffold components, such as the platform, guardrails, and anchorage points, as well as checking for any signs of damage or wear. It is important to follow a structured inspection checklist to ensure all areas are covered.
What should be included in a pre-use scaffold checklist?
A pre-use scaffold checklist should include items such as checking the stability and integrity of the scaffold, inspecting the access points and guardrails, ensuring proper planking is in place, evaluating the condition of the scaffold components, and verifying the scaffold’s load capacity.
What are some best practices for scaffold inspections?
Some best practices for scaffold inspections include conducting regular inspections, documenting the findings, and addressing any issues promptly. It is also important to ensure that inspectors are properly trained and competent in conducting scaffold inspections.
Why is it important to comply with a scaffold inspection protocol?
Following a scaffold inspection protocol is important to maintain consistency and ensure that all necessary checks are performed. It also helps with record-keeping and provides a standardized approach to scaffold inspections. Compliance with the protocol is crucial to identify and address any potential hazards or deficiencies in a timely manner.



















